Language
ENGCommon Issues with Hydraulic Hose Connectors and How to Fix Them
 2025.08.25
2025.08.25
 industy news
industy news
1. Leakage
Problem Description: Leaks in hydraulic systems often occur at fittings, hoses, fitting threads, or seals. When hydraulic oil flows under high pressure through these connections, if the fittings are not properly sealed, oil will leak. This not only reduces efficiency, but also pollutes the environment and may even damage the equipment.
Common Causes:
Deteriorated or damaged seals.
Incompatible hose and fittings, resulting in an incomplete seal.
Inadequate torque applied to threaded connections, causing the fitting to loosen.
Solution:
Inspect seals and O-rings: Seals and O-rings on hose fittings may wear or deteriorate with prolonged use. Regularly inspect these seals to ensure they are free of cracks, wear, or hardening. Replace any problems promptly.
Retighten fittings: Hydraulic fitting threads can also leak if they are not tightened to the specified torque value. Use appropriate tools (such as a torque wrench) to ensure the fittings are tightened to the specified level.
Use the appropriate fitting type: Ensure the fitting type matches the hose model. For example, threaded fittings and clamping ring fittings have different requirements. Choosing the right fitting type can significantly reduce the risk of leaks.
2. Excessive Wear or Corrosion
Problem Description: Prolonged exposure of hydraulic hose fittings to corrosive media such as hydraulic fluid, ambient moisture, salt water, or chemicals can cause corrosion or wear on the fitting surface, affecting the strength and sealing performance of the fitting. Corrosion not only shortens the fitting's service life but can also lead to more serious leaks.
Common Causes:
Corrosion caused by chemicals, salt spray, or moisture in the environment.
Hoses and fittings are not properly protected and exposed to harsh environments.
Using unsuitable fitting materials without considering environmental factors.
Solution:
Choose corrosion-resistant materials: In highly corrosive environments such as the ocean and chemical plants, use stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or coated fittings to reduce corrosion.
Inspect fittings regularly: Regularly inspect the fitting surface, especially areas susceptible to corrosion (such as the connection between the fitting and the hose), and promptly replace any corroded or worn parts.
Install protective devices: Where necessary, install protective covers or boots to protect fittings from exposure to water, moisture, or chemicals.
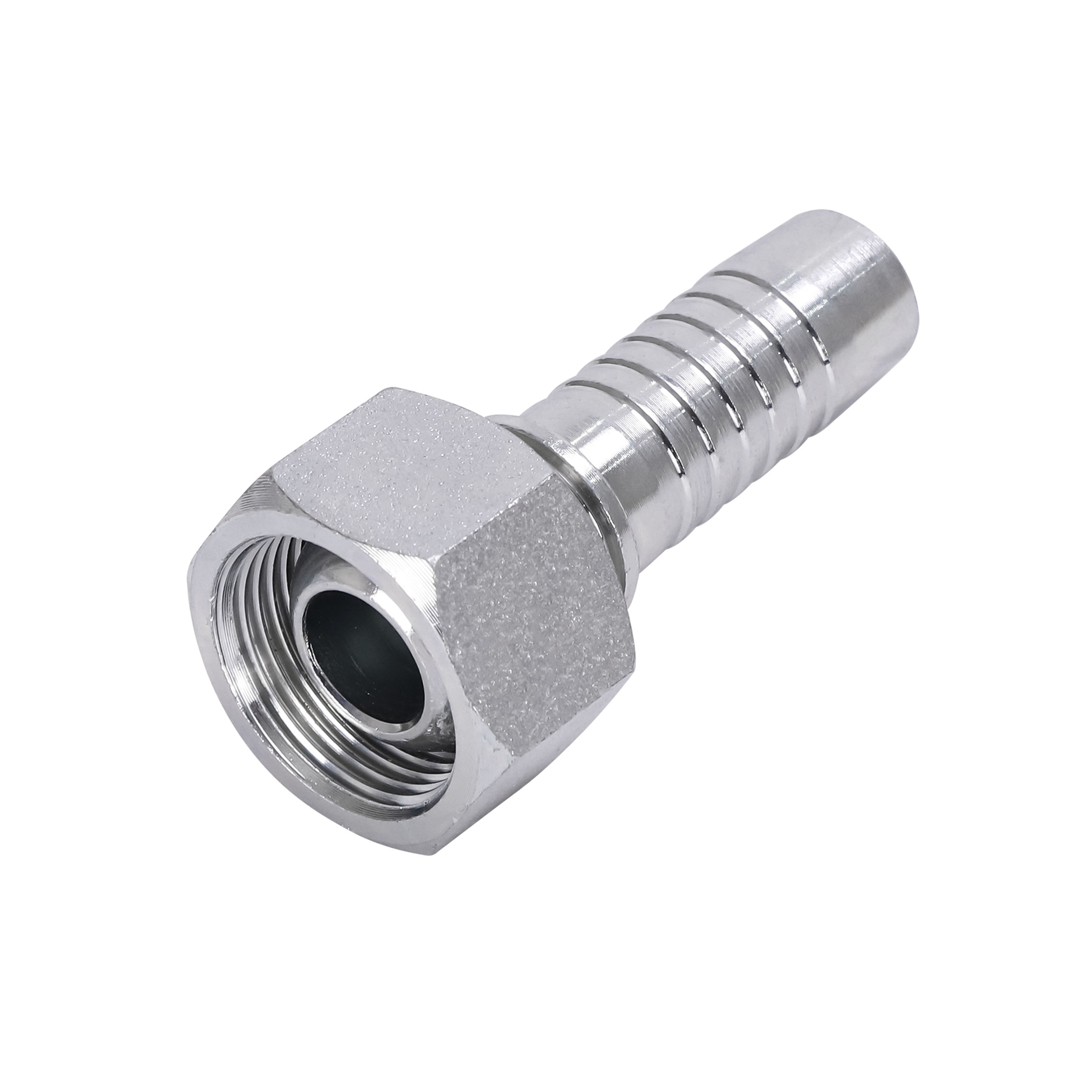

3. Excessive Vibration or Looseness
Problem Description: Hydraulic systems operating at high pressure or high speed generate significant vibration. If fittings are not securely installed, vibration can cause them to loosen, leading to leaks, breakage, or other failures. This is particularly common in environments such as machinery, ships, or mining equipment.
Common Causes:
Excessive vibration during equipment operation.
Hoses not secured or insecurely secured.
Loose connections, preventing the fittings from remaining secure.
Solution:
Secure hoses and fittings: Use hose clamps, brackets, or supports to securely secure hoses and fittings to prevent vibration-induced loosening.
Select highly vibration-resistant fittings: In high-vibration environments, choose suitable fittings, such as those with anti-loosening features or those with springs or washers.
Use anti-vibration devices: Install anti-vibration devices on vibration-prone areas of the system, such as hydraulic pumps or piping, to reduce the effects of mechanical stress.
4. Clogged Fittings
Problem Description: Clogged fittings can reduce hydraulic fluid flow or even completely block fluid flow. Blockages are often caused by contaminants, particles, or moisture in the hydraulic fluid. If not addressed promptly, this can lead to excessive system pressure and even equipment damage.
Common Causes:
Impurities or particles in the hydraulic fluid.
Failure to regularly change the hydraulic fluid, causing fluid deterioration.
Insufficient effective filtration in the system.
Solutions:
Use high-quality hydraulic fluid: Ensure the hydraulic fluid used meets specifications and avoid excessive amounts of impurities in the fluid. Change the hydraulic fluid regularly to prevent contaminant accumulation.
Install filters and filtration devices: Install effective oil filters and microfilters in the system to remove impurities and reduce the possibility of blockages. Clean or replace filters regularly.
Clean fittings regularly: Disassemble and clean hydraulic fittings to ensure they are clear. Use compressed air or cleaning agents to remove any blockages.
5. Hose and fitting mismatch
Problem Description: Hose and fitting mismatch is a major cause of leaks and failures. If the hose and fitting are not compatible in size, type, or operating pressure, the fitting will not provide an adequate seal, leading to leaks or hose rupture. Common causes:
The specifications, pressure ratings, and materials of the hose and fittings do not match.
Using an inappropriate fitting type, such as a threaded fitting with a clamping ring fitting.
The hose was not installed according to the standard during installation, resulting in an incomplete connection.
Solution:
Choose matching fittings and hoses: Ensure that the hose and fittings match in size, pressure rating, material, and other parameters. Each hose fitting corresponds to a specific model and specification.
Ensure correct installation: During installation, ensure that the fitting and hose are fully aligned to avoid misalignment. Use specialized tools during installation to ensure a correct connection.
6. Excessive operating pressure
Problem description: During hydraulic system operation, if the operating pressure exceeds the rated range of the fittings or hoses, it may cause the fittings to rupture, leak, or burst. Overpressure not only damages the fittings but can also cause failure of the entire hydraulic system.
Common causes:
The system design did not take into account possible pressure fluctuations.
The set pressure valve malfunctioned, resulting in excessive system pressure.
The fittings and hoses used are not rated for a maximum pressure rating sufficient to withstand them. Solution:
Ensure pressure matching: Select fittings and hoses that can withstand high operating pressures and match them to the system's actual operating pressure.
Install pressure control equipment: Use appropriate pressure regulating valves and pressure gauges to monitor system pressure and prevent overpressure. Set a reasonable pressure range and conduct regular inspections.
Check safety valves: Ensure all safety valves in the hydraulic system are functioning properly to prevent overpressure.
7. Thermal expansion problem
Problem description: Hydraulic oil in a hydraulic system expands at high temperatures, placing additional pressure on fittings and hoses. If the system design doesn't account for this, it can cause hose rupture, loosening of joints, or seal failure.
Common causes:
The hydraulic oil temperature in the system is too high.
The hose and fitting materials cannot withstand temperature fluctuations.
The system design was not designed to account for temperature fluctuations.
Solution:
Use high-temperature-resistant materials: Select high-temperature-resistant hoses and fittings, ensuring they can withstand hydraulic oil temperature fluctuations.
Monitor oil temperature: Install a temperature sensor in the hydraulic system to monitor the hydraulic oil temperature in real time and ensure it remains within the safe operating temperature range. Add a cooling system: If the hydraulic oil temperature is too high, you can add a radiator or cooling system to the system to reduce the oil temperature.
8. Improper Installation
Problem Description: Improper installation methods can cause poor fitting connections, increasing the risk of leaks. Common installation errors include excessive hose bends, loose fittings, or incorrect installation angles.
Common Causes:
Failure to strictly follow installation specifications.
Using inappropriate tools.
Installation at the wrong angle or position.
Solution:
Follow installation specifications: Strictly follow the manufacturer's installation instructions to ensure fittings and hoses are installed at the correct angle and position.
Use the correct tools: Use appropriate tools during installation to avoid overtightening or damaging fittings.
Avoid excessive hose bends: When installing hoses, avoid excessive bends. Maintain the natural flow of hoses and fittings to avoid twisting or stretching.














